Self-custody of cryptocurrency: A beginner's guide
As a beginner in the world of cryptocurrency, you may be wondering what self-custody means and why it's important. In this article, we'll explain the basics of self-custody and provide a step-by-step guide on how to self-custody your crypto assets.
What is self-custody?
Self-custody refers to the practice of holding and managing your own cryptocurrency assets, rather than trusting them to a third-party custodian. This means taking responsibility for the security of your assets and having complete control over them.

Self-custody has several advantages, including:
- Greater security: When you self-custody your crypto assets, you are responsible for their security. This means you can take steps to protect your assets from threats such as hackers, scams, and physical threats.
- Greater control: When you self-custody your crypto assets, you have complete control over them. This means you can make your own decisions about how to manage and use your assets, rather than relying on a third party.
- Greater privacy: When you self-custody your crypto assets, you don't have to share your personal information with a third party. This can be especially important if you value your privacy or if you are concerned about the security of your personal information.
However, self-custody also comes with some additional responsibilities and risks. It's important to be proactive in securing your assets and protecting them from threats.

Before you get started with self-custody of your crypto assets, it's important to make sure you have a secure foundation. Here are three things you should do before you begin:
- Factory reset your device and wifi router: If you're using a device or router that you've used for other purposes in the past, it's a good idea to perform a factory reset. This will erase all of the data and settings on the device, helping to ensure that it's clean and secure.
- Install security software: To protect against malware and other threats, it's important to install antivirus and other security software on your device. This can help to detect and block malicious software that could compromise your crypto assets. In addition to antivirus, it's also a good idea to install a password manager. A password manager is a tool that allows you to store multiple unique passwords in an encrypted app, rather than in your browser. This can help to protect against password-based attacks and make it easier to use strong, unique passwords for your various online accounts.
- Download genuine wallet apps from official websites: When choosing a wallet for your crypto assets, it's important to download the app from the official website of the wallet provider. This will help to ensure that you're getting a genuine, secure app that has not been tampered with. For example, you can download the official Ethereum wallet from Ethereum.org, the official Bitcoin wallet from Bitcoin.org, and the Coinbase app from Coinbase.com.
By taking these precautions, you can help to ensure that your device and network are secure and ready for self-custody of your crypto assets. Remember, the foundation of your self-custody setup is only as strong as the security of your device and network, so it's important to invest in the right tools and take the necessary precautions.

Step-by-step guide to self-custody
If you're new to self-custody, the process can seem intimidating at first. But don't worry – it's actually quite simple once you understand the basics. Here's a step-by-step guide to understanding what Steps are needed to self-custody.
Step 1: Choose a wallet
The first step in self-custodying your crypto is choosing a wallet. A wallet is a software or hardware tool that stores your cryptocurrency assets and allows you to send and receive payments.
There are several types of wallets to choose from, including:
- Hot wallets: These are wallets that are connected to the internet and are therefore more convenient for daily use. Examples include software wallets (such as a mobile or desktop wallet) like Metamask and Exodus wallet, and web-based wallets (such as an exchange wallet). However, hot wallets are also more vulnerable to security threats, so you should only keep a small amount of crypto in them.
- Cold wallets: These are wallets that are not connected to the internet and are therefore more secure. Examples include hardware wallets (such as a Trezor or Ledger) and paper wallets (such as the Shieldfolio Stonebook). Cold wallets are a good option for storing larger amounts of crypto or for long-term storage.
When choosing a wallet, consider factors such as security, ease of use, and compatibility with your crypto assets. It's also a good idea to do your research and read reviews from other users before choosing a wallet.
Step 2: Secure your wallet
Once you've chosen a wallet, the next step is to secure it. This includes:
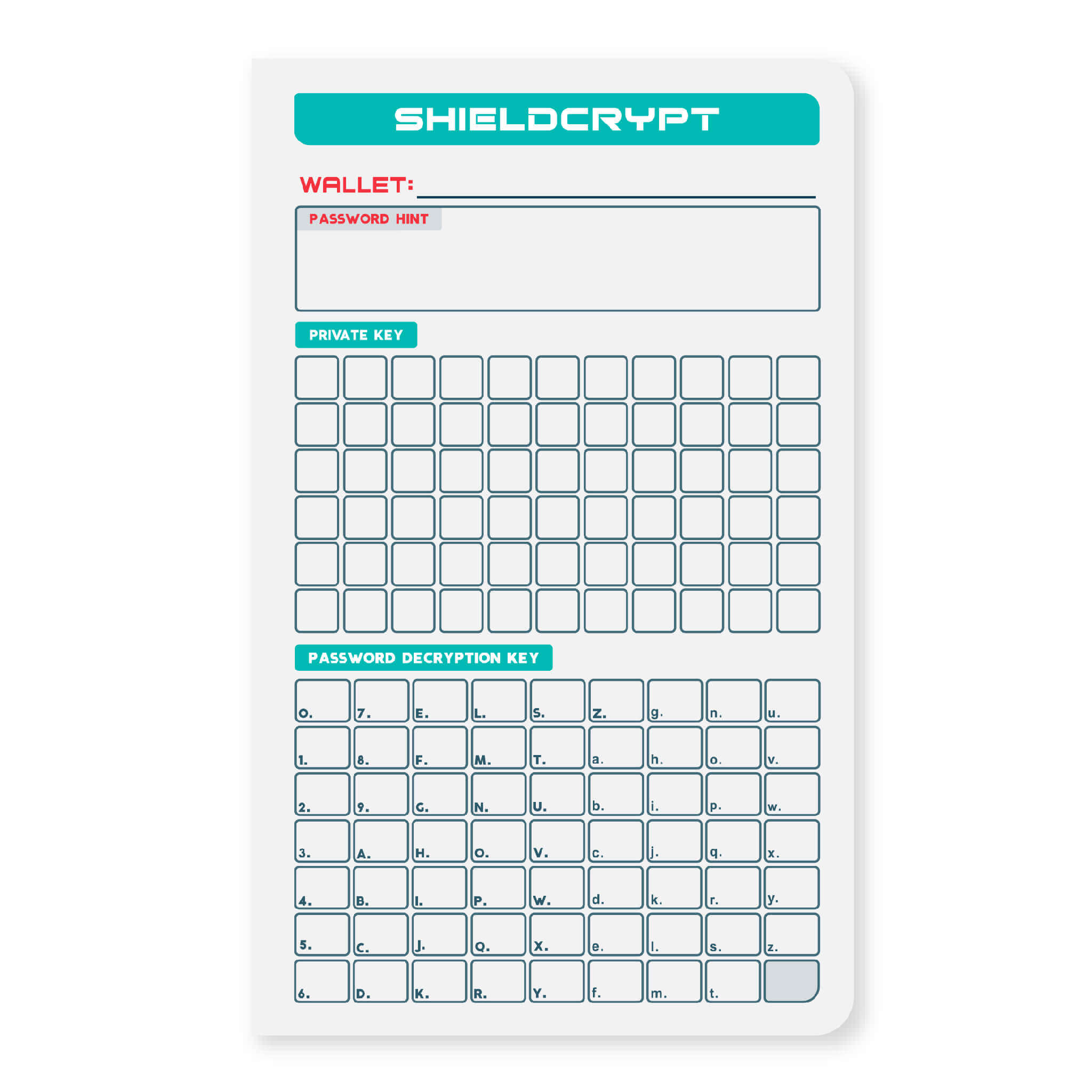
- Protecting your wallet with a strong password: Choose a password that is unique, long, and hard to guess. Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts and consider using a password manager to help you generate and store strong passwords.
- Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your wallet by requiring you to provide a second form of authentication (such as a code sent to your phone) in addition to your password when logging in or making a transaction. This makes it much harder for hackers to access your wallet.
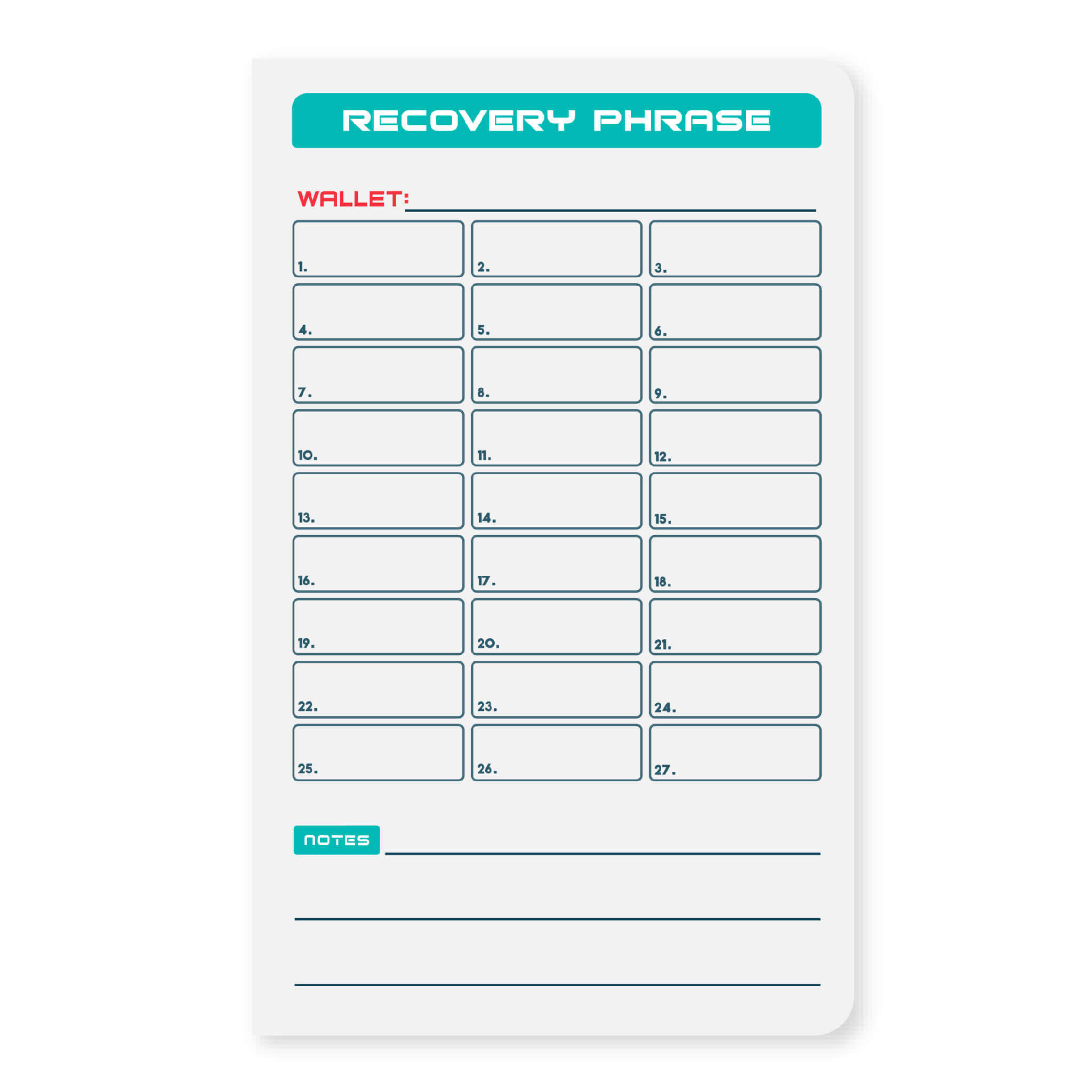
- Backing up your wallet: It's important to regularly back up your wallet to protect against the loss or destruction of your assets. This can be done through a process called seed phrase backup, which involves writing down a series of words that can be used to restore your wallet in the event that it is lost or destroyed. The Shieldfolio Stonebook is a great tool for securely storing seed phrases and other important wallet information.
Step 3: Buy and transfer crypto assets
Once you have a secure wallet set up, the next step is to buy and transfer your crypto assets. There are several ways to do this, including:
- Buying crypto from an exchange: You can buy crypto from an online exchange such as Coinbase or Binance using a credit card or bank transfer. Once you've bought the crypto, you can transfer it to your wallet.
- Receiving crypto as payment: If you are selling goods or services and want to accept crypto as payment, you can provide your wallet address to the payer. Once the payment is made, the crypto will be transferred to your wallet.
- Transferring crypto from another wallet: If you already have crypto in another wallet, you can transfer it to your new wallet by providing the receiving wallet's address.
Step 4: Keep your crypto safe
Once you have your crypto assets in your self-custodied wallet, it's important to keep them safe. Here are some tips for protecting your assets:
- Use strong passwords and enable 2FA: As mentioned above, it's important to use strong passwords and enable 2FA to protect your wallet from unauthorized access.
- Keep your software and hardware up to date: Make sure to keep your wallet software and hardware (if applicable) up to date with the latest security updates. This helps to protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers.
- Be cautious of scams and phishing attacks: Cryptocurrency scams and phishing attacks are common, so it's important to be cautious when receiving emails or messages related to your crypto assets. Never click on links or enter your password or personal information unless you are sure the source is legitimate.
- Keep your private keys private: Your private keys are the keys to your crypto assets, so it's important to keep them safe. Avoid sharing your private keys with anyone, and consider using a tool like the Shieldfolio Stonebook to securely store them.
- Follow best practices for cold and hot wallet storage: As mentioned earlier, it's a good idea to use a hot wallet for daily use and a cold wallet for long-term storage or larger amounts of crypto. This helps to balance convenience and security.
Conclusion
Self-custody of cryptocurrency is a key practice for anyone looking to take control of their crypto assets and protect them from threats. By following the steps outlined above, you can set up a secure wallet and self-custody your assets with confidence. Remember to choose a wallet that meets your needs, secure your wallet, buy and transfer crypto assets, and follow best practices for keeping your assets safe.